Health care policy is evolving, but health plans for the individual and small group markets continue to be required to offer health insurance that meets certain levels of coverage. Like those coveted Olympic medals, health plans are ranked according to their value, beginning with the bronze and climbing to the higher end platinum plan.
These values show the percentage of the total average costs for covered benefits that a plan will cover, and are designed to help individuals better understand their benefits. Use the chart below to learn more about and compare plan levels.
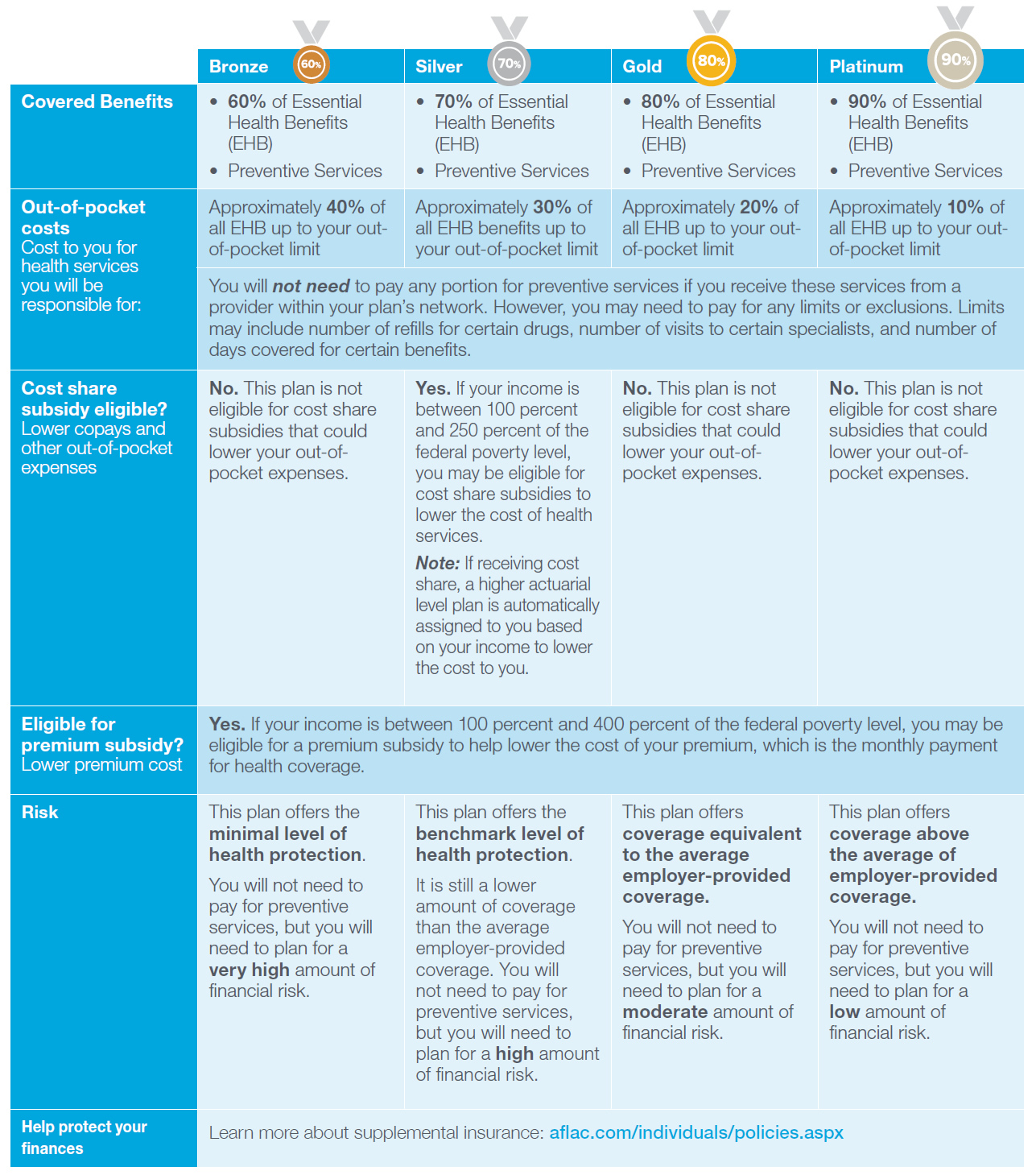
Definitions and more information:
Essential Health Benefits: A set of health care categories that must be covered by certain plans. They include:1
For more information, visit: https://www.healthcare.gov/glossary/essential-health-benefits/.
Out-of-pocket limit: Out-of-pocket limits are established annually by the IRS. These limits apply only to covered benefits, and a plan may count only in-network costs toward the out-of-pocket limit and the limit only applies to essential health benefits. If an individual or family incurs expenses for noncovered benefits, these will not count toward their out-of-pocket limit, adding to potential unexpected costs.
Out-of-pocket costs: Your expenses for medical care that aren't reimbursed by insurance. Out-of-pocket costs include deductibles, coinsurance, and copayments for covered services plus all costs for services that aren't covered.1
Preventive Services: Routine health care that includes screenings, checkups and patient counseling to prevent illnesses, disease or other health problems.1 For more information visit: http://www.hhs.gov/healthcare/rights/preventive-care/index.html.
Premium: The amount that must be paid for your health insurance or plan. You and/or your employer usually pay it monthly, quarterly or yearly.1
Federal Poverty Level: A measure of income level issued annually by the Department of Health and Human Services. Federal poverty levels are used to determine your eligibility for certain programs and benefits.1
Supplemental insurance: With plans available to fit most budgets, supplemental insurance policies such as accident, hospital and disability insurance pay cash benefits for covered illnesses or injuries. These plans are designed to help you with out-of-pocket costs that major medical insurance was never intended to cover.
This material is intended to provide general information about an evolving topic and does not constitute legal, tax or accounting advice regarding any specific situation. Aflac cannot anticipate all the facts that a particular employer or individual will have to consider in their benefits decision-making process. We strongly encourage readers to discuss their HCR situations with their advisors to determine the actions they need to take or to visit healthcare.gov (which may also be contacted at 1-800-318-2596) for additional information.
Z181545
EXP 12/19